Hello, wonderful readers! Today, let's embark on a fun adventure into the world of matrices and how they make Machine Learning even more magical. If you're new to this, fear not! We'll breeze through it together, step by step. We will learn their fundamental properties, advanced concepts and practical examples. By the end, you'll not only comprehend matrices but also wield them adeptly in problem-solving scenarios.
Matrices: A Closer Look
Imagine you have a magic box filled with numbers. Now, let's organize these numbers neatly into rows and columns, just like a grid. Voilà! You've created a matrix.
Rows and Columns
In our magical matrix world, each row represents a set of related values, while each column represents a specific attribute or characteristic. For example, let's consider a matrix representing information about houses:
Size Location Age
1500 1 5
2000 2 10
1800 3 8
Each row corresponds to a house, with columns representing features like size, location, and age.
Size Matters: Dimensions of a Matrix
Matrices come in all shapes and sizes. We measure the size of a matrix by counting its rows and columns. So, if a matrix has 3 rows and 3 columns, we call it a 3x3 matrix

Elements: The Building Blocks
Now, let's zoom in on each little square in our matrix grid. These squares are called elements. Each element holds a specific value, like a number or a symbol. For example, in the matrix above, the element in the first row and second column is "1", representing the location of the first house.
Not Just Numbers: Types of Matrices
Matrices aren't just about numbers; they come in all sorts of flavours! Some matrices are filled with real numbers, while others might contain symbols or even equations. For example ->
Identity Matrix
An identity matrix is a square matrix where all the elements on the main diagonal (from the top-left to the bottom-right) are equal to 1, and all other elements are equal to 0.

Diagonal Matrix
A diagonal matrix is a square matrix where all the elements off the main diagonal are zero.

Symmetric Matrix
A symmetric matrix is a square matrix that is equal to its transpose. In other words, for any element A[i][j], A[j][i] = A[i][j]

Upper Triangular Matrix
An upper triangular matrix is a square matrix where all the elements below the main diagonal are zero

Lower Triangular Matrix
A lower triangular matrix is a square matrix where all the elements above the main diagonal are zero

Zero Matrix
A zero matrix is a matrix where all the elements are zero

These are some common types of matrices, each with its own characteristics and applications. Understanding these types can be helpful in various mathematical and computational contexts.
Matrix Operations: Transforming Data
Matrix operations are like magic spells that allow us to manipulate and transform our data in fascinating ways. Here are some of the most common operations:
Addition and Subtraction:
We can add or subtract matrices of the same size by simply adding or subtracting corresponding elements

Scalar Multiplication:
We can multiply a matrix by a scalar (a single number) by multiplying every element of the matrix by that scalar.
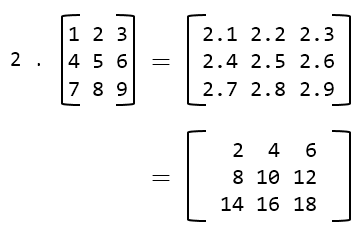
Matrix Multiplication:
Matrix multiplication is a bit more complex. When multiplying two matrices, the number of columns in the first matrix must be equal to the number of rows in the second matrix. The resulting matrix has the same number of rows as the first matrix and the same number of columns as the second matrix.
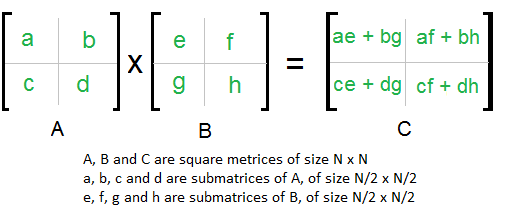
Applications: Where Matrices Shine
Matrices aren't just fancy grids; they're powerful tools with endless applications. From solving systems of equations to representing geometric transformations, matrices pop up everywhere in math, science, and of course, Machine Learning! They're like the Swiss Army knives of mathematics—versatile, reliable, and always ready to tackle any problem.
Sorting Things Out: Data Organization
Imagine you have a bunch of data lying around—like information about houses, people, or even cats! Matrices help us tidy up this data in a neat and tidy way. For example, if we have info on 100 houses, each with 5 features, we can neatly arrange it into a 100x5 matrix. This makes it super easy to play around with the data and crunch numbers.
Shaping the World: Linear Transformations
Matrices aren't just for organizing data; they're also like magic wands for transforming stuff. Think of them as the wizards of Machine Learning! With matrices, we can do all sorts of cool tricks, like turning images from one color to another or squeezing lots of info into fewer dimensions. It's like the ultimate makeover for data!
Tackling Big Jobs: Crunching Numbers with Large Datasets
Ever tried juggling a gazillion numbers all at once? It's not easy! But with matrices, we can do it like pros. They help us zip through calculations, even when we're dealing with massive amounts of data. So, whether we're multiplying matrices or doing other math stuff, matrices make it all feel like a breeze.
Now, let's put all this matrix magic into action with a fun example!
Some more applications in real-world scenarios
Computer Graphics: Matrices are extensively used in computer graphics for transformations like translation, rotation, scaling, and projection. They help in rendering 3D objects on a 2D screen.
Economics and Finance: Matrices are used in economic models to represent input-output relationships, such as Leontief's input-output model. In finance, matrices are employed for portfolio optimization, risk assessment, and analyzing financial data.
Engineering: Matrices are used in structural analysis to represent the stiffness and flexibility of structures. They are also utilized in electrical engineering for circuit analysis and in signal processing for filtering and transformations.
Statistics: Matrices are employed in statistical analysis for methods like linear regression, multivariate analysis, and factor analysis. They help in organizing and manipulating data efficiently.
Physics: Matrices play a crucial role in quantum mechanics, representing physical observables as Hermitian matrices and quantum states as vectors. They are also used in classical mechanics for solving systems of equations.
Operations Research: Matrices are extensively used in operations research for modeling optimization problems, such as linear programming and transportation problems.
Biology and Bioinformatics: Matrices are used in bioinformatics for sequence alignment and analyzing genetic data. In neuroscience, matrices are used to represent connectivity patterns in the brain.
Image and Signal Processing: Matrices are used to represent images and signals in digital form. Operations such as filtering, compression, and enhancement are performed using matrix manipulation techniques.
Markov Chains: Matrices are used to model stochastic processes like Markov chains, which find applications in various fields such as genetics, finance, and telecommunications.
Machine Learning and Data Mining: Matrices are fundamental in machine learning for representing datasets and mathematical models. Techniques like principal component analysis (PCA) and singular value decomposition (SVD) heavily rely on matrix operations.
Conclusion
So, there you have it—a closer look at the fascinating world of matrices! These humble grids may seem simple at first glance, but they're the building blocks of so many amazing things. By understanding matrices and their intricacies, you're unlocking a world of possibilities in math, science, and beyond. So, keep exploring, keep learning, and keep unleashing the power of matrices in everything you do! 🌟
