Unveiling the Core Concepts and Applications of Linear Algebra in Machine Learning
Fundamental Concepts of Linear Algebra
Linear algebra is the secret weapon of machine learning. It helps algorithms manipulate data like pros, efficiently. In this comprehensive guide, we dive into the fundamentals to better understand how it powers machine learning. Let's dig in!
Vectors
Vectors are mathematical objects that represent quantities with both magnitude and direction.
They are commonly used in Machine Learning to represent features or data points in a high-dimensional space.
Vectors are indispensable for representing features or data points within high-dimensional spaces, facilitating algorithmic analysis and interpretation.
Practical Application:
In machine learning, vectors are used to represent features of data points. Each data point is represented as a vector where each dimension corresponds to a specific feature.
For example, in a dataset of images, each image can be represented as a vector where each dimension represents the intensity of a pixel. Similarly, in text classification, each document can be represented as a vector where each dimension represents the frequency of a particular word.
Matrices
Matrices are rectangular arrays of numbers, often used to represent linear transformations or systems of linear equations.
They are fundamental in linear algebra and have various applications in Machine Learning, such as in data pre-processing and dimensionality reduction techniques.
They are used for data pre-processing, dimensionality reduction, and various other tasks.
Practical Application:
In machine learning, datasets are commonly represented as matrices, where each row corresponds to an observation and each column corresponds to a feature. For example, in a dataset of house prices, each row could represent a house, and each column could represent features such as the number of bedrooms, square footage, and location.
Matrices enable efficient manipulation and analysis of datasets, facilitating tasks such as data pre-processing, feature engineering, and model training.
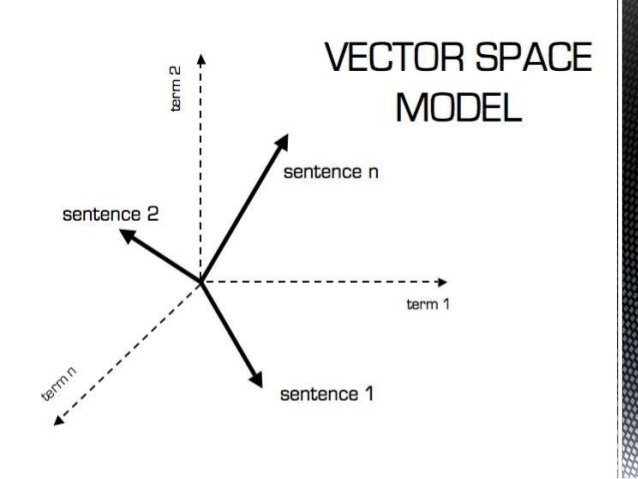
Vector Spaces
Vector spaces are sets of vectors that satisfy certain properties, such as closure under addition and scalar multiplication.
These spaces are pivotal for understanding linear transformations and eigenvalues, pivotal concepts in machine learning.
Practical Application:
Vector spaces allow us to analyze the linear independence of features. Linearly independent features provide unique information, while linearly dependent features can introduce redundancy.
Machine learning models can be represented and manipulated as vectors in a vector space. For example, the parameters of a linear regression model form a vector in the parameter space, and the predictions of the model can be represented as vectors in the output space.
Linear Transformations
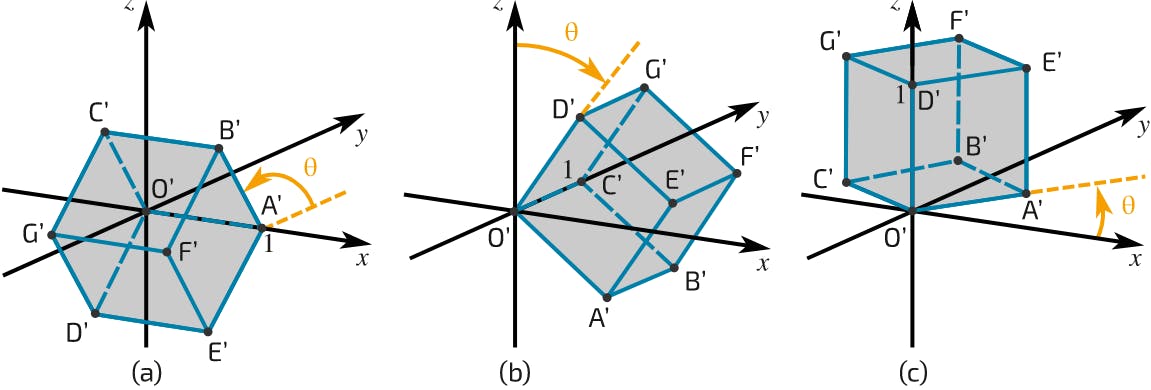
Linear transformations are functions that preserve vector addition and scalar multiplication.
They are used to describe and analyze the relationship between vectors and matrices in linear algebra, and are fundamental in understanding concepts such as eigenvectors and eigenvalues.
Practical Application:
Linear transformations such as rotation, scaling, and translation are applied to images to perform operations like image transformation, cropping, and resizing.
In signal processing applications, linear transformations are used to filter and manipulate signals.